Biologically Active Molecules
Various bioactive molecules have been isolated and/or synthesized to be used in products for food and drug industry. Our work involves development of selective isolation methods, preferentially using nontoxic solvents such as carbon dioxide and water, for making antioxidants, vitamins, essential oils and other important plant components. Identification of those species is performed using chromatographic techniques with mass spectrometric detection.
Determination of Resveratrol and its Metabolites in Serum and Liver Samples
Trans-resveratrol (RES), a naturally occurring molecule found in many foods, has been associated with a variety of beneficial biological activities, including anti-cancer, analgesic, and cardio- and neuro-protective processes. Methods using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization (ESI) have previously been employed to detect and quantify RES in blood and tissue samples; however, the ESI conditions were not optimized for the highest sensitivity. The goal is to present an optimization of chromatographic and ESI conditions using design of experiments (DOE) with liquid chromatography-high resolution time of flight mass spectrometry (ESI-LC-HR-TOF MS) to measure the levels of RES and two metabolites in rat serum and liver samples.
Determination of Celecoxib in Human Plasma Samples
A sensitive method for determination of Celecoxib (CXB) in human plasma samples was developed using liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization and time of flight mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-TOF-MS). A full factorial design of experiments (FF-DOE) methodology was applied to optimize the ESI conditions for CXB determination and also to predict the effects of interactions of multiple parameters affecting ionization (i.e., capillary voltage, fragmentor voltage, electrolyte and electrolyte concentration). The optimum ionization voltages were 4500V and 220V for capillary and fragmentor, respectively. Even though the highest ESI efficiency was obtained without electrolytes, the addition of 1.0mM ammonium acetate was shown to be essential to buffer the matrix effect and ensure a consistent response. In contrast to previous studies, deuterated CXB was used as a recovery (surrogate) standard, which enabled the correction of CXB loss during sample preparation. The extraction recovery using solid phase extraction was 87-98%. The instrumental limit of detection of CXB (LOD), 0.33ng/mL, and matrix affected LOD, 0.55ng/mL, were similar and comparable to the previously reported LC-MS/MS LODs. This method was employed to determine CXB concentrations in human plasma samples. Upon administration of 400mg CXB to healthy women, the concentrations found in the plasma were 440-3300ng/mL. The inter-day repeatability was less than 4% RSD.
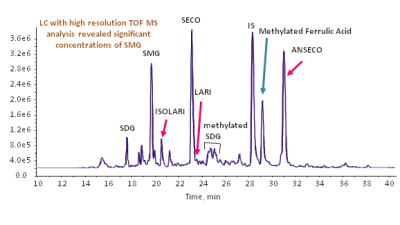
Determination of Lignans in Flaxseed